Plant Physiol :山东大学、山东省农科院丨线粒体丙酮酸载体调控植物耐镉的机理(附NMT实验体系)
转自中关村旭月非损伤微测技术产业联盟

- 期刊:Plant Physiology
- 主题:线粒体丙酮酸载体调控植物耐镉的机理
- 标题:Mitochondrial Pyruvate Carriers Prevent Cadmium Toxicity by Sustaining the TCA Cycle and Glutathione Synthesis
- 影响因子:5.949
- 检测指标:Cd2+流速
- 检测部位:拟南芥根(距离根尖400μm)
- Cd2+流速流实验处理方法:拟南芥种子萌发3天后,50μMCdCl2处理7天
- Cd2+流速流实验测试液成份:0.1 mM KCl, 0.05 mM CdCl2, 0.3 mM MES, pH 5.8
- 作者:山东大学、山东省农科院张伟、高建伟、贺立龙
英文摘要
Cadmium (Cd) is a major heavy metal pollutant, and Cd toxicity is a serious cause of abiotic stress in the environment. Plants protect themselves against Cd stress through a variety of pathways.
In a recent study, we found that mitochondrial pyruvate carriers (MPCs) are involved in Cd tolerance in Arabidopsis (Arabidopsis thaliana). Following the identification of MPCs in yeast (Saccharomyces cerevisiae) in 2012, most studies have focused on the function of MPCs in animals, as a possible approach to reduce the risk of cancer developing.
The results of this study show that AtMPC protein complexes are required for Cd tolerance and prevention of Cd accumulation in Arabidopsis. AtMPC complexes are composed of two elements, AtMPC1 and AtMPC2 (AtNRGA1 or AtMPC3). When the formation of AtMPCs was interrupted by the loss of AtMPC1, glutamate could supplement the synthesis of acetyl-coenzyme A and sustain the TCA cycle. With the up-regulation of glutathione synthesis following exposure to Cd stress, the supplementary pathway could not efficiently drive the tricarboxylic acid cycle without AtMPC. The ATP content decreased concomitantly with the deletion of tricarboxylic acid activity, which led to Cd accumulation in Arabidopsis.
More importantly, ScMPCs were also required for Cd tolerance in yeast. Our results suggest that the mechanism of Cd tolerance may be similar in other species.
中文摘要(谷歌机翻)
镉(Cd)是一种主要的重金属污染物,Cd毒性是环境中非生物胁迫的严重原因。植物通过各种途径保护自己免受Cd胁迫。
在最近的一项研究中,我们发现线粒体丙酮酸载体(MPCs)参与拟南芥(Arabidopsis thaliana)的Cd耐受。继2012年在酵母(酿酒酵母)中鉴定MPC后,大多数研究都集中在MPCs在动物体内的功能,作为降低癌症发展风险的可能方法。
该研究的结果表明,AtMPC蛋白复合物是拟南芥中Cd耐受和预防Cd积累所必需的。AtMPC复合物由两种元素组成,AtMPC1和AtMPC2(AtNRGA1或AtMPC3)。当AtMPC的形成中断AtMPC的形成时,谷氨酸可以补充乙酰辅酶A的合成并维持TCA循环。随着暴露于Cd胁迫后谷胱甘肽合成的上调,补充途径不能在没有AtMPC的情况下有效地驱动三羧酸循环。随着三羧酸活性的缺失,ATP含量同时下降,导致拟南芥中Cd的积累。
更重要的是,ScMPCs也是酵母中Cd耐受性所必需的。我们的研究结果表明,其他物种的镉耐受机制可能相似。
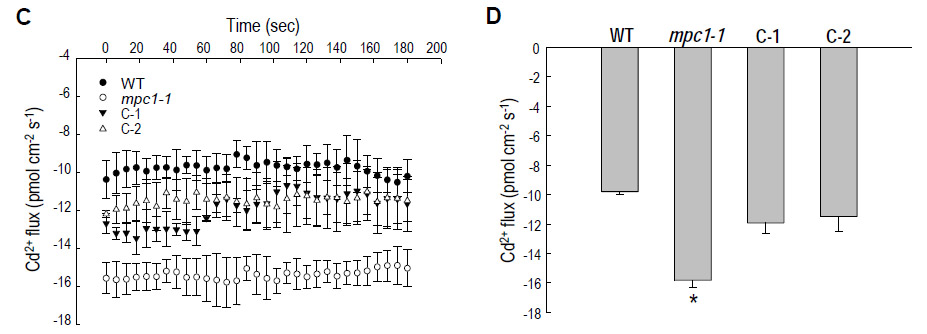
结果表明:结果表明:在50μMCdCl2处理下,mpc1-1根系中的Cd2+吸收远高于野生型和互补株系(图C和D)。
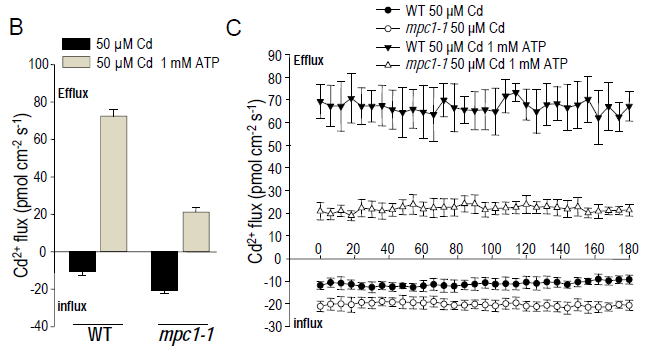
结果表明:通过在野生型和mpc1-1的根中添加1mM ATP,Cd2+吸收受到显着影响并变为外排。此外,野生型的Cd2+流速变化比mpc1-1更明显。野生型Cd2+流速从大约-10pmolcm-2s-1变为70pmol cm-2s-1,而mpc1-1从大约-20pmolcm-2s-1变为20pmol cm-2s-1(图b和c)。在MPC存在下,ATP有助于Cd2+的外排。
文章链接:http://www.plantphysiol.org/content/180/1/198








